<< precession | precipitation | precision-approach radar >>
Back to: "P"
precipitation
- Definição1
- Precipitation is a hydrometeor consisting of water particles, liquid or solid, that fall from the atmosphere and reach the ground.
- Fonte1
- INTERNATIONAL CIVIL AVIATION ORGANIZATION. Manual of runway visual range observing and reporting practices. 3. ed. Montreal, 2005. (Doc. 9328)
- Fonte2
- WORLD METEOROLOGICAL ORGANIZATION. Guide to meteorological instruments and methods of observation. 7th ed. Geneva, 2006. (WMO, n.8).
- Fonte3
- AMERICAN METEOROLOGICAL SOCIETY. Glossary of meteorology. [S.l., última modificação 05 oct. 2015]. Disponível em: < http://glossary.ametsoc.org/wiki/Main_Page >. Acesso em: 22 mar. 2022.
- Nota Adicional1
- Precipitation includes drizzle, rain, snow, snow grains, ice crystals (diamond dust), ice pellets, hail, small hail and/or snow pellets.
- Nota Adicional2
- As this is usually measured in a fixed rain gauge, small amounts of dew, frost, rime, etc., may be included in the total. The more common term rainfall is also used in this total sense to include not only amounts of rain, but also the water equivalents of frozen precipitation. For obvious reasons, precipitation is the preferred general term.
- Contexto
- The character of precipitation can be defined as being one of three forms, namely showers, intermittent precipitation, and continuous precipitation. Showers are those precipitation events associated with physically-separated convective clouds. Observers (or instruments replacing humans) also have to classify precipitation into the three intensity categories: light, moderate, and heavy, according to the rates of precipitation fall or other related factors (such as visibility).
- Subárea
- Aeronautical Meteorology
- Related Term
- heavy rain
- shower
- Français
- précipitation
- Imagem
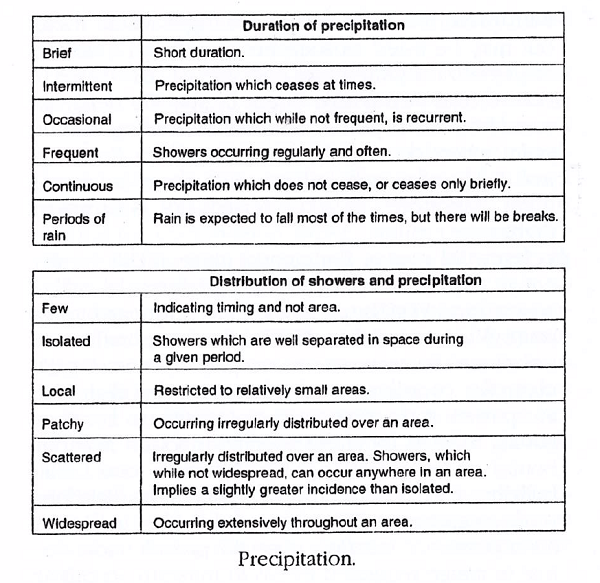
Precipitation.
Source: KUMAR, Bharat (ed.). An illustrated dictionary of aviation. New York: McGraw-Hill, c2005. 752 p.

