<< pre-flight information bulletin | precession | precipitation >>
Back to: "P"
precession
- Definição1
- One of the two basic characteristics of a gyroscope. The other basic characteristic is rigidity in space. Precession causes a force applied to a spinning gyroscope to be felt, not at the point the force is applied, but at a point 90º in the direction of rotation from that point.
- Fonte1
- CRANE, Dale (ed.). Dictionary of aeronautical terms. 2nd ed. Renton: ASA, 1991.
- Fonte2
- FEDERAL AVIATION ADMINISTRATION. Rotorcraft flying handbook (FAA-H-8083-21). Washington, DC: FAA, 2000. Disponível em: http://www.faa.gov/library/manuals/aircraft/media/faa-h-8083-21.pdf. Acesso em: 10 fev. 2012.
- Contexto
- Precession is the tilting or turning of a gyro in response to pressure. The reaction to this pressure does not occur at the point where it was applied; rather, it occurs at a point that is 90° later in the direction of rotation from where the pressure was applied. This principle allows the gyro to determine a rate of turn by sensing the amount of pressure created by a change in direction. Precession can also create some minor errors in some instruments.
- Subárea
- Aerodynamics
- Français
- précession
- Imagem
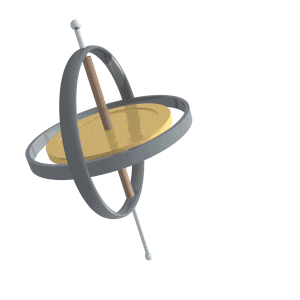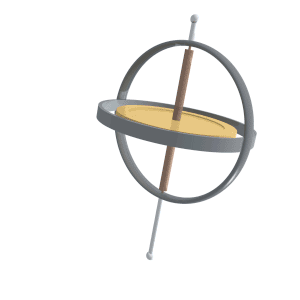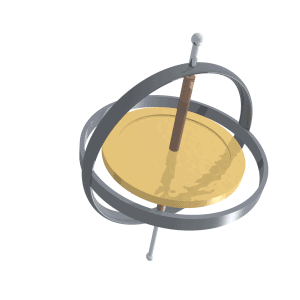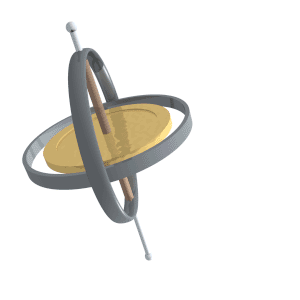
Precession of a gyroscope.
Fonte: https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/8/82/Gyroscope_precession.gif

