<< volcanic (ash) cloud | volcanic ash | volcanic ash advisory centre >>
Back to: "V"
volcanic ash
- Fonte1
- INTERNATIONAL CIVIL AVIATION ORGANIZATION. Flight safety and volcanic ash: risk management of flight operations with known or forecast volcanic ash contamination. Advance edition (unedited). Montreal, 2012. (Doc. 9974)
- Fonte2
- INTERNATIONAL CIVIL AVIATION ORGANIZATION. Air traffic services: annex 11 to the Convention on International Civil Aviation. 3rd ed. Montreal, 2001.
- Fonte3
- WORLD METEOROLOGICAL ORGANIZATION. Manual on codes: international codes: volume I.2: annex II to the WMO technical regulations: parte B: binary codes. parte C: common features to binary and alphanumeric codes. Geneva, 2015. (WMO, n.306).
- Fonte4
- INTERNATIONAL CIVIL AVIATION ORGANIZATION. Manual on Volcanic Ash, Radioactive Material and Toxic Chemical Clouds. Third edition. Montreal, 2015. (Doc. 9691).
- Nota adicional1
- Volcanic ash (VA), when expected, is always forecast regardless of visibility.
- Nota adicional2
- Volcanic Ash is comprised of minerals unique to the volcanic eruption. Minerals common to most volcanic ash are silica together with smaller amounts of the oxides of aluminium, iron, calcium and sodium. The glassy silicate material is very hard and extremely abrasive. Its melting point is below jet engine burner temperature which introduces additional hazards.
- Contexto
- Close coordination shall be maintained between area control centres, flight information centres and associated meteorological watch offices to ensure that information on volcanic ash included in NOTAM and SIGMET messages is consistent.
- In addition to volcanic ash, volcanic eruption columns also contain many gases including water vapour, sulphur dioxide, chlorine, hydrogen sulphide and oxides of nitrogen. While the proportion of each of these gases in particular volcanic eruptions varies widely, the predominant constituent gases are water vapour, sulphur dioxide and chlorine. In their gaseous form these constituents of the volcanic ash cloud are not thought to cause significant harmful effects to aircraft.
- Subárea1
- Aeronautical Meteorology
- Related Term
- volcanic (ash) cloud
- volcanic ash advisory centre
- volcanic ash advisory information
- Português
- cinzas vulcânicas
- Imagem

Austral’s Embraer 190 covered in volcaninc ash at Bariloche airport, Argentina.
Fonte: IDIARTE, Marcelo. O problema das cinzas vulcânicas. In: CAVOK: asas da informação, jun. 2011. Disponível em: http://www.cavok.com.br/blog/o-problema-das-cinzas-vulcanicas/. Acesso em: 20 maio 2015.
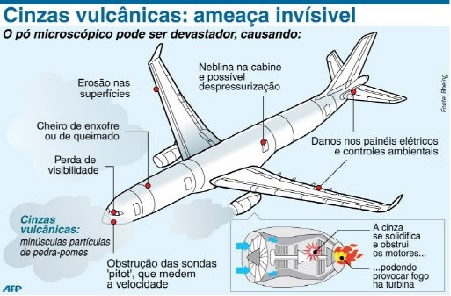
Volcanic ash: invisible threat. The microscopic powder can be devastating.
Fonte: IDIARTE, Marcelo. O problema das cinzas vulcânicas. In: CAVOK: asas da informação, jun. 2011. Disponível em: http://www.cavok.com.br/blog/o-problema-das-cinzas-vulcanicas/. Acesso em: 20 maio 2015.

