- Definição1
- A precision instrument approach system that normally consists of the following electronic components and visual aids; localizer, glide slope, outer marker, middle marker, and approach lights.
- Fonte1
- FEDERAL AVIATION ADMINISTRATION. Instrument procedures handbook: FAA-H-8261-1A. 2nd ed. Newcastle: ASA, 2007.
- Definição2
- A radio aid to navigation intended to facilitate aircraft in landing. It provides lateral and vertical guidance to the optimum point of landing. The various components of an instrument landing system are the localizer, which guides the aircraft to the centerline of the runway; a glide-slope transmitter, which guides the aircraft along the required guide path; outer and inner markers, which indicate to the aircraft that it is passing overhead them; and the airport lighting system.
- Fonte2
- KUMAR, Bharat (ed.). An illustrated dictionary of aviation. New York: McGraw-Hill, c2005. 752 p.
- Fonte3
- AGÊNCIA NACIONAL DE AVIAÇÃO CIVIL. RBAC 01: regulamentos brasileiros de aviação civil. Definições, regras de redação e unidades de medida. [S.l.], 2008. (Regulamentos Brasileiros de Aviação Civil)
- Fonte4
- INTERNATIONAL CIVIL AVIATION ORGANIZATION. Aircraft accident digest n.26. Montreal, 1983. (Cir. 173 AN/109).
- Nota adicional1
- Acronym in English: ILS.
- Nota adicional2
- ILS CATEGORIES- 1. Category I. An ILS approach procedure which provides for approach to a height above touchdown of not less than 200 feet and with runway visual range of not less than 1,800 feet.- 2.?Special Authorization Category I. An ILS approach procedure which provides for approach to a height above touchdown of not less than 150 feet and with runway visual range of not less than 1,400 feet, HUD to DH. 3. Category II. An ILS approach procedure which provides for approach to a height above touchdown of not less than 100 feet and with runway visual range of not less than 1,200 feet (with autoland or HUD to touchdown and noted on authorization, RVR 1,000 feet).- 4. Special Authorization Category II with Reduced Lighting. An ILS approach procedure which provides for approach to a height above touchdown of not less than 100 feet and with runway visual range of not less than 1,200 feet with autoland or HUD to touchdown and noted on authorization (no touchdown zone and centerline lighting are required).- 5. Category III: a.IIIA.-An ILS approach procedure which provides for approach without a decision height minimum and with runway visual range of not less than 700 feet. b.IIIB.-An ILS approach procedure which provides for approach without a decision height minimum and with runway visual range of not less than 150 feet. c.IIIC.-An ILS approach procedure which provides for approach without a decision height minimum and without runway visual range minimum.
- Nota adicional3
- ILS (instrument landing systems) are categorized according to their capability to provide for approach to a height above touchdown (HAT)/decision height (DH) and RVR (runway visual range).
- Nota adicional4
- Information regarding this term is a result of researches developed by DECEA in cooperation with ANAC.
- Contexto
- The National Transportation Safety Board determined that the probable cause of this incident was the unavailability to the flightcrew of timely information concerning a rapidly changing weather environment along the instrument landing system final approach course.
- Português
- sistema de pouso por instrumentos
- Imagem
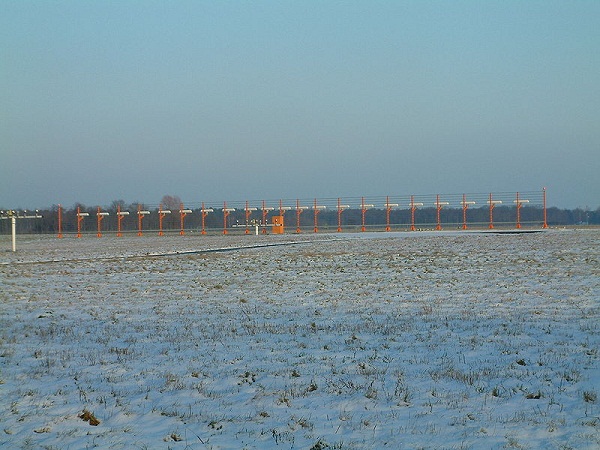

ILS Localizer 21-element dipole reflector antenna array, Runway 27R, EDDV Hanover/Langenhagen International Airport. The picture shows the back of the antenna system.
Fonte: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:EDDV-ILS_27R_Localizer.jpg
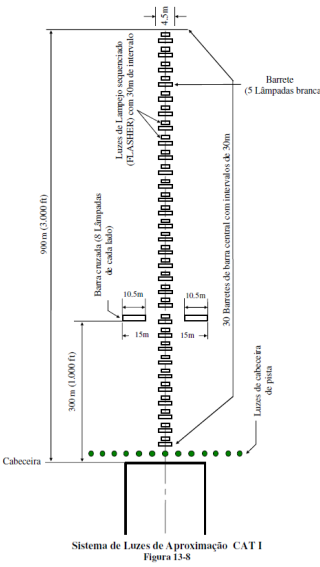
Instrument landing system category I.
Fonte: BRASIL. Comando da Aeronáutica. Departamento de Controle do Espaço Aéreo. MANINV-BRASIL: manual brasileiro de inspeção em voo. Rio de Janeiro, 2005. Disponível em: http://publicacoes.decea.gov.br/view.cfm?id=2755. Acesso em: 10 jun. 2014.
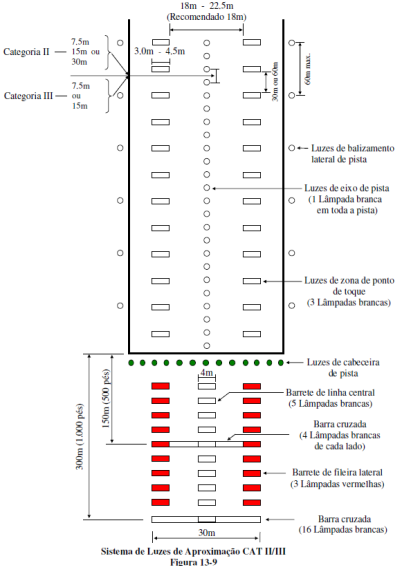
Instrument landing system category II and category III.
Fonte: BRASIL. Comando da Aeronáutica. Departamento de Controle do Espaço Aéreo. MANINV-BRASIL: manual brasileiro de inspeção em voo. Rio de Janeiro, 2005. Disponível em: http://publicacoes.decea.gov.br/view.cfm?id=2755. Acesso em: 10 jun. 2014.
<< instrument flight time | instrument landing system | instrument meteorological conditions >>
Back to: "I"
instrument landing system

