Back to: "B"
BWB
- Usado para
- blended wing body
- Definição1
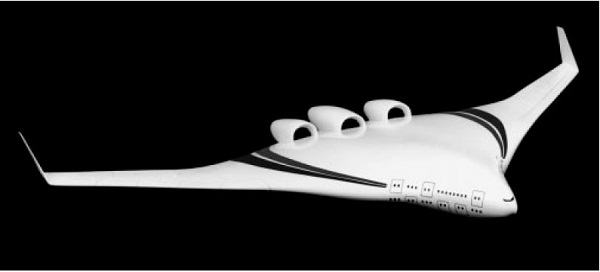
- Aircraft in which wing/fuselage intersections are eliminated.
- Fonte1
- GUNSTON, Bill. The Cambridge aerospace dictionary. Cambridge: Cambridge University, 2004. (Cambridge aerospace series.)
- Fonte2
- INTERNATIONAL CIVIL AVIATION ORGANIZATION. Report to CAEP by the CAEP noise technology independent expert panel: aircraft noise technology review and medium and long term noise reduction goals: report. Montreal, 2010. (Doc. 9943)
- Fonte3
- INTERNATIONAL CIVIL AVIATION ORGANIZATION. Report by the second CAEP noise technology independent expert panel: novel aircraft-noise technology review and medium- and long-term noise reduction goals: report. Montreal, 2014. (Doc. 10017)
- Contexto
- Most of the novel airframe/engine concepts currently being developed and evaluated within the aviation industry today have to be viewed as one integrated system and cannot strictly be assessed separately. The low noise characteristics of these concepts are partly due to the shielding of the engine noise (fan inlet, fan exhaust, core and jet) by the Blended-Wing-Body (BWB) and partly airframe noise reduction features such as low noise landing gear and the omission of flaps.
- The configurations have been broken into three categories. The first category covers conventional tube-wing aircraft, which are designs that have a traditional passenger aircraft layout where the wings are cantilever mounted to the airframe and the engines are hung from the wings. The second category presents novel tube-wing configurations that deviate from the traditional tube-wing design, but still have a tail for aircraft control. The third category presents tail-less aircraft such as the blended wing body, hybrid wing body, and the flying wing.
- Subárea1
- Aircraft
- Português
- BWB
- Imagem